Overview
Components
The Miden client currently has two main components:
Miden client library
The Miden client library is a Rust library that can be integrated into projects, allowing developers to interact with the Miden rollup.
The library provides a set of APIs and functions for executing transactions, generating proofs, and managing activity on the Miden network.
Miden client CLI
The Miden client also includes a command-line interface (CLI) that serves as a wrapper around the library, exposing its basic functionality in a user-friendly manner.
The CLI provides commands for interacting with the Miden rollup, such as submitting transactions, syncing with the network, and managing account data.
Software prerequisites
- Rust installation minimum version 1.85.
Install the client
We currently recommend installing and running the client with the concurrent feature.
Run the following command to install the miden-client:
cargo install miden-cli --features concurrent
This installs the miden binary (at ~/.cargo/bin/miden) with the concurrent feature.
Concurrent feature
The concurrent flag enables optimizations that result in faster transaction execution and proving times.
Run the client
-
Make sure you have already installed the client. If you don't have a
miden-client.tomlfile in your directory, create one or runmiden initto initialize one at the current working directory. You can do so without any arguments to use its defaults or define either the RPC endpoint or the store config via--networkand--store-path -
Run the client CLI using:
miden
The Miden client offers a range of functionality for interacting with the Miden rollup.
Transaction execution
The Miden client facilitates the execution of transactions on the Miden rollup; allowing users to transfer assets, mint new tokens, and perform various other operations.
Proof generation
The Miden rollup supports user-generated proofs which are key to ensuring the validity of transactions on the Miden rollup.
To enable such proofs, the client contains the functionality for executing, proving, and submitting transactions.
Miden network interactivity
The Miden client enables users to interact with the Miden network. This includes syncing with the latest blockchain data and managing account information.
Account generation and tracking
The Miden client provides features for generating and tracking accounts within the Miden rollup ecosystem. Users can create accounts and track their transaction status.
The Miden client has the following architectural components:
tip
- The RPC client and the store are Rust traits.
- This allow developers and users to easily customize their implementations.
Store
The store is central to the client's design.
It manages the persistence of the following entities:
- Accounts; including their state history and related information such as vault assets and account code.
- Transactions and their scripts.
- Notes.
- Note tags.
- Block headers and chain information that the client needs to execute transactions and consume notes.
Because Miden allows off-chain executing and proving, the client needs to know about the state of the blockchain at the moment of execution. To avoid state bloat, however, the client does not need to see the whole blockchain history, just the chain history intervals that are relevant to the user.
The store can track any number of accounts, and any number of notes that those accounts might have created or may want to consume.
RPC client
The RPC client communicates with the node through a defined set of gRPC methods.
Currently, these include:
GetBlockHeaderByNumber: Returns the block header information given a specific block number.SyncState: Asks the node for information relevant to the client. For example, specific account changes, whether relevant notes have been created or consumed, etc.SubmitProvenTransaction: Sends a locally-proved transaction to the node for inclusion in the blockchain.
Transaction executor
The transaction executor executes transactions using the Miden VM.
When executing, the executor needs access to relevant blockchain history. The executor uses a DataStore interface for accessing this data. This means that there may be some coupling between the executor and the store.
note
For a complete example on how to run the client and submit transactions to the Miden node, refer to the Getting started documentation.
This section shows you how to get started with Miden by generating a new Miden account, requesting funds from a public faucet, consuming private notes, and creating public pay-to-id-notes.
By the end of this tutorial, you will have:
- Configured the Miden client.
- Connected to a Miden node.
- Created an account and requested funds from the faucet.
- Transferred assets between accounts by creating and consuming notes.
Prerequisites
Rust
Download from the Rust website.
In this section, we show you how to create a new local Miden account and how to receive funds from the public Miden faucet website.
Configure the Miden client
The Miden client facilitates interaction with the Miden rollup and provides a way to execute and prove transactions.
Tip Check the Miden client documentation for more information.
-
If you haven't already done so as part of another tutorial, open your terminal and create a new directory to store the Miden client.
mkdir miden-client cd miden-client -
Install the Miden client.
cargo install miden-cli --features concurrentYou can now use the
miden --versioncommand, and you should seeMiden 0.9.0. -
Initialize the client. This creates the
miden-client.tomlfile.miden init --network testnet # Creates a miden-client.toml configured with the testnet node's IP
Create a new Miden account
-
Create a new account of type
mutableusing the following command:miden new-wallet --mutable -
List all created accounts by running the following command:
miden account -lYou should see something like this:

Save the account ID for a future step.
Request tokens from the public faucet
-
To request funds from the faucet navigate to the following website: Miden faucet website.
-
Copy the Account ID printed by the
miden account -lcommand in the previous step. Feel free to change the amount of tokens to issue. -
Paste this ID into the Request test tokens input field on the faucet website and click Send Private Note.
Tip You can also click Send Public Note. If you do this, the note's details will be public and you will not need to download and import it, so you can skip to Sync the client.
-
After a few seconds your browser should download - or prompt you to download - a file called
note.mno(mno = Miden note). It contains the funds the faucet sent to your address. -
Save this file on your computer, you will need it for the next step.
Import the note into the Miden client
-
Import the private note that you have received using the following commands:
miden import <path-to-note>/note.mno -
You should see something like this:
Successfully imported note 0x0ff340133840d35e95e0dc2e62c88ed75ab2e383dc6673ce0341bd486fed8cb6 -
Now that the note has been successfully imported, you can view the note's information using the following command:
miden notes -
You should see something like this:

Tip: The importance of syncing
- As you can see, the note is listed as
Expected.- This is because you have received a private note but have not yet synced your view of the rollup to check that the note is the result of a valid transaction.
- Hence, before consuming the note we will need to update our view of the rollup by syncing.
- Many users could have received the same private note, but only one user can consume the note in a transaction that gets verified by the Miden operator.
Sync the client
Do this periodically to keep informed about any updates on the node by running the sync command:
miden sync
You will see something like this as output:
State synced to block 179672
New public notes: 0
Tracked notes updated: 1
Tracked notes consumed: 0
Tracked accounts updated: 0
Commited transactions: 0
Consume the note & receive the funds
-
Now that we have synced the client, the input-note imported from the faucet should have a
Committedstatus, confirming it exists at the rollup level:miden notes -
You should see something like this:

-
Find your account and note id by listing both
accountsandnotes:miden account miden notes -
Consume the note and add the funds from its vault to our account using the following command:
miden consume-notes --account <Account-Id> <Note-Id> -
You should see a confirmation message like this:
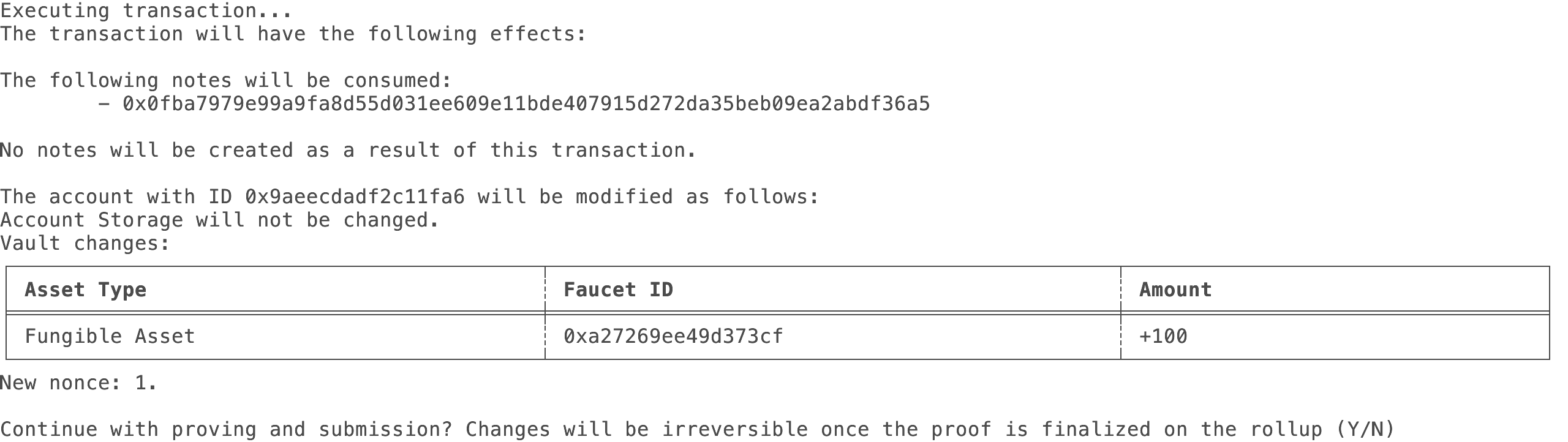
-
After confirming you can view the new note status by running the following command:
miden notes -
You should see something like this:

-
The note is
Processing. This means that the proof of the transaction was sent, but there is no network confirmation yet. You can update your view of the rollup by syncing again:miden sync -
After syncing, you should have received confirmation of the consumed note. You should see the note as
Consumedafter listing the notes:miden notes
Amazing! You just have created a client-side zero-knowledge proof locally on your machine and submitted it to the Miden rollup.
Tip You only need to copy the top line of characters of the Note ID.
View confirmations
-
View your updated account's vault containing the tokens sent by the faucet by running the following command:
miden account --show <Account-Id> -
You should now see your accounts vault containing the funds sent by the faucet.
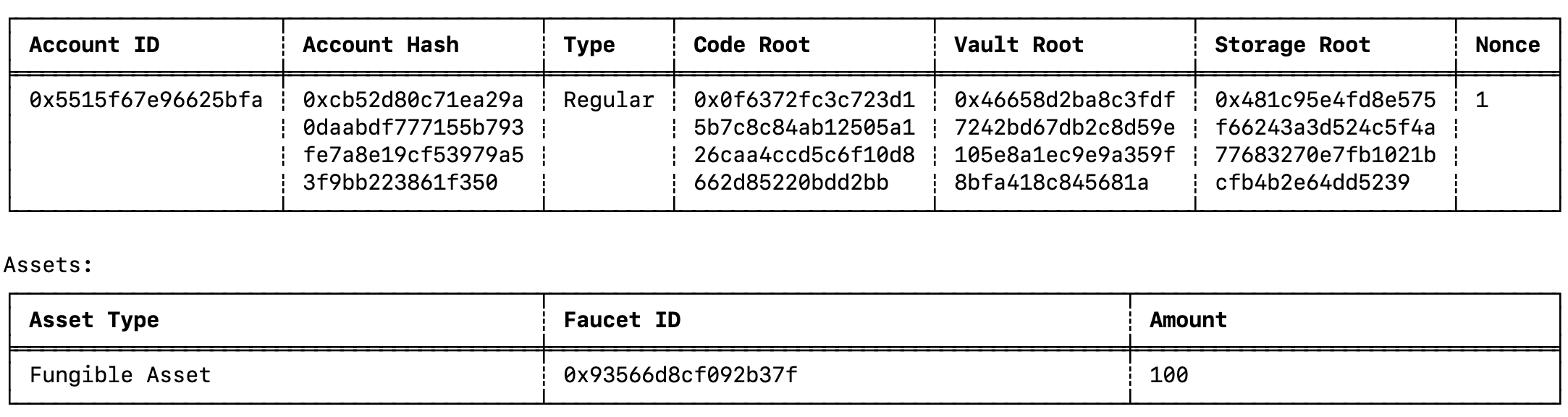
Congratulations!
You have successfully configured and used the Miden client to interact with a Miden rollup and faucet.
You have performed basic Miden rollup operations like submitting proofs of transactions, generating and consuming notes.
For more information on the Miden client, refer to the Miden client documentation.
Debugging tips (clear state and folder)
-
Need a fresh start? All state is maintained in
store.sqlite3, located in the directory defined in themiden-client.tomlfile. If you want to clear all state, delete this file. It recreates on any command execution. -
Getting an error? Only execute the
miden-clientcommand in the folder where yourmiden-client.tomlis located.
In this section, we show you how to execute transactions and send funds to another account using the Miden client and public notes.
Important: Prerequisite steps
- You should have already followed the prerequisite steps and get started documents.
- You should have not reset the state of your local client.
Create a second client
Tip Remember to use the Miden client documentation for clarifications.
This is an alternative to the private P2P transactions process.
In this tutorial, we use two different clients to simulate two different remote users who don't share local state.
To do this, we use two terminals with their own state (using their own miden-client.toml).
-
Create a new directory to store the new client.
mkdir miden-client-2 cd miden-client-2 -
Initialize the client. This creates the
miden-client.tomlfile line-by-line.miden init --network testnet # Creates a miden-client.toml file configured with the testnet node's IP -
On the new client, create a new basic account:
miden new-wallet --mutable -s publicWe refer to this account as Account C. Note that we set the account's storage mode to
public, which means that the account details are public and its latest state can be retrieved from the node. -
List and view the account with the following command:
miden account -l
Transfer assets between accounts
-
Now we can transfer some of the tokens we received from the faucet to our new account C. Remember to switch back to
miden-clientdirectory, since you'll be making the txn from Account ID A.To do this, from the first client run:
miden send --sender <basic-account-id-A> --target <basic-account-id-C> --asset 50::<faucet-account-id> --note-type publicNote The faucet account id is
0xad904b3138d71d3eand can also be found on the Miden faucet website under the title Miden faucet.This generates a Pay-to-ID (
P2ID) note containing50tokens, transferred from one account to the other. As the note is public, the second account can receive the necessary details by syncing with the node. -
First, sync the account on the new client.
miden sync -
At this point, we should have received the public note details.
miden notes --listBecause the note was retrieved from the node, the commit height will be included and displayed.
-
Have account C consume the note.
miden consume-notes --account <regular-account-ID-C> <input-note-id>Tip It's possible to use a short version of the note id: 7 characters after the
0xis sufficient, e.g.0x6ae613a.
That's it!
Account C has now consumed the note and there should be new assets in the account:
miden account --show <account-ID>
Clear state
All state is maintained in store.sqlite3, located in the directory defined in the miden-client.toml file.
To clear all state, delete this file. It recreates on any command execution.
In this section, we show you how to make private transactions and send funds to another account using the Miden client.
Important: Prerequisite steps
- You should have already followed the prerequisite steps and get started documents.
- You should not have reset the state of your local client.
Create a second account
Tip Remember to use the Miden client documentation for clarifications.
-
Create a second account to send funds with. Previously, we created a type
mutableaccount (account A). Now, create anothermutable(account B) using the following command:miden new-wallet --mutable -
List and view the newly created accounts with the following command:
miden account -l -
You should see two accounts:
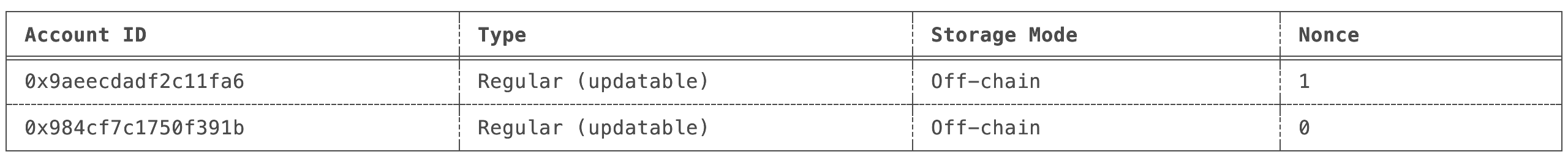
Transfer assets between accounts
-
Now we can transfer some of the tokens we received from the faucet to our second account B.
To do this, run:
miden send --sender <regular-account-id-A> --target <regular-account-id-B> --asset 50::<faucet-account-id> --note-type privateNote The faucet account id can be found on the Miden faucet website under the title Miden faucet.
This generates a private Pay-to-ID (
P2ID) note containing50assets, transferred from one account to the other. -
First, sync the accounts.
miden sync -
Get the second note id.
miden notes -
Have the second account consume the note.
miden consume-notes --account <regular-account-ID-B> <input-note-id>Tip It's possible to use a short version of the note id: 7 characters after the
0xis sufficient, e.g.0x6ae613a.You should now see both accounts containing faucet assets with amounts transferred from
Account AtoAccount B. -
Check the second account:
miden account --show <regular-account-ID-B>
-
Check the original account:
miden account --show <regular-account-ID-A>
Wanna do more? Sending public notes
Congratulations!
You have successfully configured and used the Miden client to interact with a Miden rollup and faucet.
You have performed basic Miden rollup operations like submitting proofs of transactions, generating and consuming notes.
For more information on the Miden client, refer to the Miden client documentation.
Clear data
All state is maintained in store.sqlite3, located in the directory defined in the miden-client.toml file.
To clear all state, delete this file. It recreates on any command execution.
To use the Miden client library in a Rust project, include it as a dependency.
In your project's Cargo.toml, add:
miden-client = { version = "0.9" }
Features
The Miden client library supports the concurrent feature which is recommended for developing applications with the client. To use it, add the following to your project's Cargo.toml:
miden-client = { version = "0.9", features = ["concurrent"] }
The library also supports several other features. Please refer to the crate's documentation to learn more.
Client instantiation
Spin up a client using the following Rust code and supplying a store and RPC endpoint.
Create local account
With the Miden client, you can create and track any number of public and local accounts. For local accounts, the state is tracked locally, and the rollup only keeps commitments to the data, which in turn guarantees privacy.
The AccountBuilder can be used to create a new account with the specified parameters and components. The following code creates a new local account:
Once an account is created, it is kept locally and its state is automatically tracked by the client.
To create an public account, you can specify AccountStorageMode::Public like so:
let key_pair = SecretKey::with_rng(client.rng());
let anchor_block = client.get_latest_epoch_block().await.unwrap();
let (new_account, seed) = AccountBuilder::new(init_seed) // Seed should be random for each account
.anchor((&anchor_block).try_into().unwrap())
.account_type(AccountType::RegularAccountImmutableCode)
.storage_mode(AccountStorageMode::Public)
.with_component(RpoFalcon512::new(key_pair.public_key()))
.with_component(BasicWallet)
.build()?;
client.add_account(&new_account, Some(seed), &AuthSecretKey::RpoFalcon512(key_pair), false).await?;
The account's state is also tracked locally, but during sync the client updates the account state by querying the node for the most recent account data.
Execute transaction
In order to execute a transaction, you first need to define which type of transaction is to be executed. This may be done with the TransactionRequest which represents a general definition of a transaction. Some standardized constructors are available for common transaction types.
Here is an example for a pay-to-id transaction type:
You can decide whether you want the note details to be public or private through the note_type parameter.
You may also execute a transaction by manually defining a TransactionRequest instance. This allows you to run custom code, with custom note arguments as well.
The following document lists the commands that the CLI currently supports.
tip
Use --help as a flag on any command for more information.
Usage
Call a command on the miden-client like this:
miden <command> <flags> <arguments>
Optionally, you can include the --debug flag to run the command with debug mode, which enables debug output logs from scripts that were compiled in this mode:
miden --debug <flags> <arguments>
Note that the debug flag overrides the MIDEN_DEBUG environment variable.
Commands
init
Creates a configuration file for the client in the current directory.
# This will create a config file named `miden-client.toml` using default values
# This file contains information useful for the CLI like the RPC provider and database path
miden init
# You can set up the CLI for any of the default networks
miden init --network testnet # This is the default value if no network is provided
miden init --network devnet
miden init --network localhost
# You can use the --network flag to override the default RPC config
miden init --network 18.203.155.106
# You can specify the port
miden init --network 18.203.155.106:8080
# You can also specify the protocol (http/https)
miden init --network https://18.203.155.106
# You can specify both
miden init --network https://18.203.155.106:1234
# You can use the --store_path flag to override the default store config
miden init --store_path db/store.sqlite3
# You can provide both flags
miden init --network 18.203.155.106 --store_path db/store.sqlite3
account
Inspect account details.
Action Flags
| Flags | Description | Short Flag |
|---|---|---|
--list | List all accounts monitored by this client | -l |
--show <ID> | Show details of the account for the specified ID | -s |
--default <ID> | Manage the setting for the default account | -d |
The --show flag also accepts a partial ID instead of the full ID. For example, instead of:
miden account --show 0x8fd4b86a6387f8d8
You can call:
miden account --show 0x8fd4b86
For the --default flag, if <ID> is "none" then the previous default account is cleared. If no <ID> is specified then the default account is shown.
new-wallet
Creates a new wallet account.
A basic wallet is comprised of a basic authentication component (for RPO Falcon signature verification), alongside a basic wallet component (for sending and receiving assets).
This command has three optional flags:
--storage-mode <TYPE>: Used to select the storage mode of the account (private if not specified). It may receive "private" or "public".--mutable: Makes the account code mutable (it's immutable by default).--extra-components <TEMPLATE_FILES_LIST>: Allows to pass a list of account component template files which can be added to the account. If the templates contain placeholders, the CLI will prompt the user to enter the required data for instantiating storage appropriately.
After creating an account with the new-wallet command, it is automatically stored and tracked by the client. This means the client can execute transactions that modify the state of accounts and track related changes by synchronizing with the Miden network.
new-account
Creates a new account and saves it locally.
An account may be composed of one or more components, each with its own storage and distinct functionality. This command lets you build a custom account by selecting an account type and optionally adding extra component templates.
This command has four flags:
--storage-mode <STORAGE_MODE>: Specifies the storage mode of the account. It accepts either "private" or "public", with "private" as the default.--account-type <ACCOUNT_TYPE>: Specifies the type of account to create. Accepted values are:fungible-faucetnon-fungible-faucetregular-account-immutable-coderegular-account-updatable-code
--component-templates <COMPONENT_TEMPLATES>: Allows you to provide a list of file paths for account component template files to include in the account. These components are looked up from your configuredcomponent_template_directoryfield inmiden-client.toml.--init-storage-data-path <INIT_STORAGE_DATA_PATH>: Specifies an optional file path to a TOML file containing key/value pairs used for initializing storage. Each key should map to a placeholder within the provided component templates. The CLI will prompt for any keys that are not present in the file.
After creating an account with the new-account command, the account is stored locally and tracked by the client, enabling it to execute transactions and synchronize state changes with the Miden network.
Examples
# Create a new wallet with default settings (private storage, immutable, no extra components)
miden new-wallet
# Create a new wallet with public storage and a mutable code
miden new-wallet --storage-mode public --mutable
# Create a new wallet that includes extra components from local templates
miden new-wallet --extra-components template1,template2
# Create a fungible faucet with interactive input
miden new-account --account-type fungible-faucet -c basic-fungible-faucet
# Create a fungible faucet with preset fields
miden new-account --account-type fungible-faucet --component-templates basic-fungible-faucet --init-storage-data-path init_data.toml
info
View a summary of the current client state.
notes
View and manage notes.
Action Flags
| Flags | Description | Short Flag |
|---|---|---|
--list [<filter>] | List input notes | -l |
--show <ID> | Show details of the input note for the specified note ID | -s |
The --list flag receives an optional filter:
- expected: Only lists expected notes.
- committed: Only lists committed notes.
- consumed: Only lists consumed notes.
- processing: Only lists processing notes.
- consumable: Only lists consumable notes. An additional --account-id <ID> flag may be added to only show notes consumable by the specified account.
If no filter is specified then all notes are listed.
The --show flag also accepts a partial ID instead of the full ID. For example, instead of:
miden notes --show 0x70b7ecba1db44c3aa75e87a3394de95463cc094d7794b706e02a9228342faeb0
You can call:
miden notes --show 0x70b7ec
sync
Sync the client with the latest state of the Miden network. Shows a brief summary at the end.
tags
View and add tags.
Action Flags
| Flag | Description | Aliases |
|---|---|---|
--list | List all tags monitored by this client | -l |
--add <tag> | Add a new tag to the list of tags monitored by this client | -a |
--remove <tag> | Remove a tag from the list of tags monitored by this client | -r |
tx
View transactions.
Action Flags
| Command | Description | Aliases |
|---|---|---|
--list | List tracked transactions | -l |
After a transaction gets executed, two entities start being tracked:
- The transaction itself: It follows a lifecycle from
Pending(initial state) andCommitted(after the node receives it). It may also beDiscardedif the transaction was not included in a block. - Output notes that might have been created as part of the transaction (for example, when executing a pay-to-id transaction).
Transaction creation commands
mint
Creates a note that contains a specific amount tokens minted by a faucet, that the target Account ID can consume.
Usage: miden mint --target <TARGET ACCOUNT ID> --asset <AMOUNT>::<FAUCET ID> --note-type <NOTE_TYPE>
consume-notes
Account ID consumes a list of notes, specified by their Note ID.
Usage: miden consume-notes --account <ACCOUNT ID> [NOTES]
For this command, you can also provide a partial ID instead of the full ID for each note. So instead of
miden consume-notes --account <some-account-id> 0x70b7ecba1db44c3aa75e87a3394de95463cc094d7794b706e02a9228342faeb0 0x80b7ecba1db44c3aa75e87a3394de95463cc094d7794b706e02a9228342faeb0
You can do:
miden consume-notes --account <some-account-id> 0x70b7ecb 0x80b7ecb
Additionally, you can optionally not specify note IDs, in which case any note that is known to be consumable by the executor account ID will be consumed.
Either Expected or Committed notes may be consumed by this command, changing their state to Processing. It's state will be updated to Consumed after the next sync.
send
Sends assets to another account. Sender Account creates a note that a target Account ID can consume. The asset is identified by the tuple (FAUCET ID, AMOUNT). The note can be configured to be recallable making the sender able to consume it after a height is reached.
Usage: miden send --sender <SENDER ACCOUNT ID> --target <TARGET ACCOUNT ID> --asset <AMOUNT>::<FAUCET ID> --note-type <NOTE_TYPE> <RECALL_HEIGHT>
swap
The source account creates a SWAP note that offers some asset in exchange for some other asset. When another account consumes that note, it will receive the offered asset amount and the requested asset will removed from its vault (and put into a new note which the first account can then consume). Consuming the note will fail if the account doesn't have enough of the requested asset.
Usage: miden swap --source <SOURCE ACCOUNT ID> --offered-asset <OFFERED AMOUNT>::<OFFERED FAUCET ID> --requested-asset <REQUESTED AMOUNT>::<REQUESTED FAUCET ID> --note-type <NOTE_TYPE>
Tips
For send and consume-notes, you can omit the --sender and --account flags to use the default account defined in the config. If you omit the flag but have no default account defined in the config, you'll get an error instead.
For every command which needs an account ID (either wallet or faucet), you can also provide a partial ID instead of the full ID for each account. So instead of
miden send --sender 0x80519a1c5e3680fc --target 0x8fd4b86a6387f8d8 --asset 100::0xa99c5c8764d4e011
You can do:
miden send --sender 0x80519 --target 0x8fd4b --asset 100::0xa99c5c8764d4e011
!!! note The only exception is for using IDs as part of the asset, those should have the full faucet's account ID.
Transaction confirmation
When creating a new transaction, a summary of the transaction updates will be shown and confirmation for those updates will be prompted:
miden <tx command> ...
TX Summary:
...
Continue with proving and submission? Changes will be irreversible once the proof is finalized on the rollup (Y/N)
This confirmation can be skipped in non-interactive environments by providing the --force flag (miden send --force ...):
Importing and exporting
export
Export input note data to a binary file .
| Flag | Description | Aliases |
|---|---|---|
--filename <FILENAME> | Desired filename for the binary file. | -f |
--export-type <EXPORT_TYPE> | Exported note type. | -e |
Export type
The user needs to specify how the note should be exported via the --export-type flag. The following options are available:
id: Only the note ID is exported. When importing, if the note ID is already tracked by the client, the note will be updated with missing information fetched from the node. This works for both public and private notes. If the note isn't tracked and the note is public, the whole note is fetched from the node and is stored for later use.full: The note is exported with all of its information (metadata and inclusion proof). When importing, the note is considered unverified. The note may not be consumed directly after importing as its block header will not be stored in the client. The block header will be fetched and be used to verify the note during the next sync. At this point the note will be committed and may be consumed.partial: The note is exported with minimal information and may be imported even if the note is not yet committed on chain. At the moment of importing the note, the client will check the state of the note by doing a note sync, using the note's tag. Depending on the response, the note will be either stored as "Expected" or "Committed".
import
Import entities managed by the client, such as accounts and notes. The type of entities is inferred.
Executing scripts
exec
Execute the specified program against the specified account.
| Flag | Description | Aliases |
|---|---|---|
--account <ACCOUNT_ID> | Account ID to use for the program execution. | -a |
--script-path <SCRIPT_PATH> | Path to script's source code to be executed. | -s |
--inputs-path <INPUTS_PATH> | Path to the inputs file. | -i |
--hex-words | Print the output stack grouped into words. |
After installation, use the client by running the following and adding the relevant commands:
miden
tip
Run miden --help for information on miden commands.
Client Configuration
We configure the client using a TOML file (miden-client.toml).
[rpc]
endpoint = { protocol = "http", host = "localhost", port = 57291 }
timeout_ms = 10000
[store]
database_filepath = "store.sqlite3"
[cli]
default_account_id = "0x012345678"
The TOML file should reside in same the directory from which you run the CLI.
In the configuration file, you will find a section for defining the node's rpc endpoint and timeout and the store's filename database_filepath.
By default, the node is set up to run on localhost:57291.
note
- Running the node locally for development is encouraged.
- However, the endpoint can point to any remote node.
There's an additional optional section used for CLI configuration. It currently contains the default account ID, which is used to execute transactions against it when the account flag is not provided.
By default none is set, but you can set and unset it with:
miden account --default <ACCOUNT_ID> #Sets default account
miden account --default none #Unsets default account
note
The account must be tracked by the client in order to be set as the default account.
You can also see the current default account ID with:
miden account --default
Environment variables
MIDEN_DEBUG: When set totrue, enables debug mode on the transaction executor and the script compiler. For any script that has been compiled and executed in this mode, debug logs will be output in order to facilitate MASM debugging (these instructions can be used to do so). This variable can be overridden by the--debugCLI flag.